How Long Do Ants Live
What’s the Lifespan of an Ant?
There are a handful of factors, from species of ant to an ant’s caste within an ant colony, that affect how long an ant’s lifespan is. The largest determining factor within a specific species is the ant caste, or the specific role, an ant plays within a colony. An ant’s caste is largely determined by a combination of genetics from the ant queen and care provided by the worker ants who feed the developing ant larvae. The ant queen contributes to ant caste determination through selective fertilization while worker ants ensure that ant larvae are provided with the right nutrients to become the ant caste that is needed to ensure the survival of the any colony. The different castes within an ant colony each have a different lifespan. The ant queen can survive for several decades depending on the species, with the oldest known ant queen living over 20 years. The rest of the different ants’ lifespans vary depending on the role they play.
Ant Life Cycle
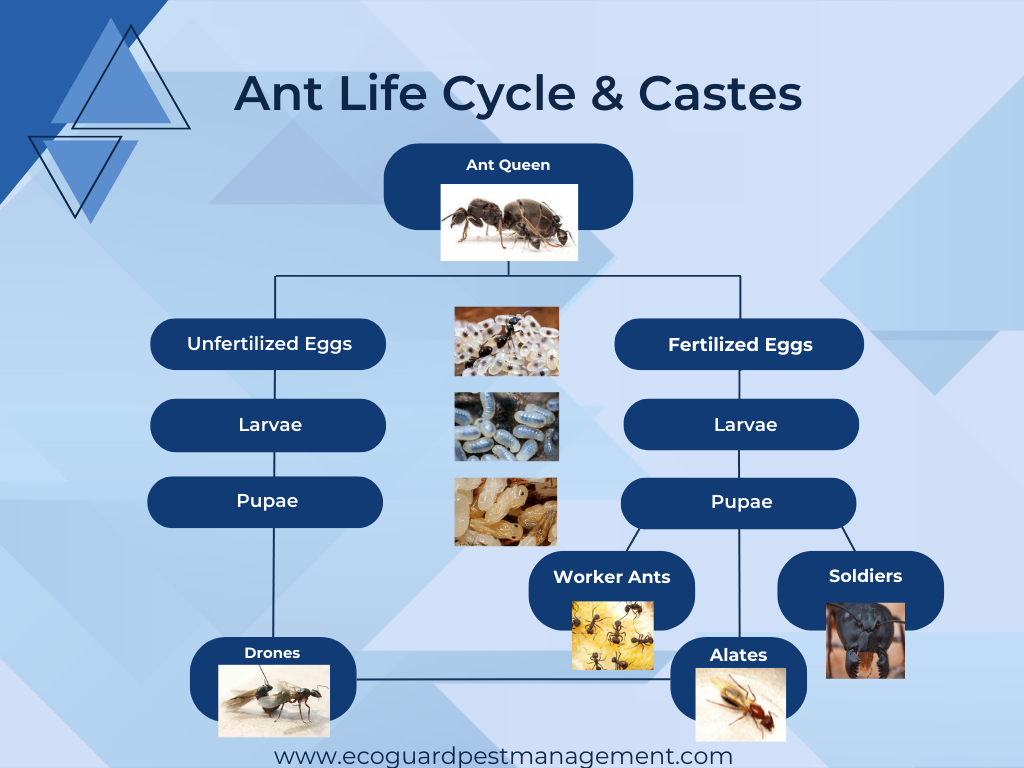
Understanding an ant’s lifespan starts with understanding the life cycle of an ant. The reason behind this is because the average lifespan of ants is largely dependent on the caste outcome that is determined as an ant develops into adulthood. There are several stages of the ant life cycle that play a critical role in ant caste selection.
Ant Eggs: An ant’s life begins as an egg. This stage of the ant’s lifecycle typically lasts 1 - 2 weeks before hatching. The first stage of caste selection occurs when eggs are laid. Eggs that are selected to be fertilized by the ant queen will become female workers, soldiers, or alates while unfertilized eggs turn into male drones. The ant queen has the ability to fertilize the eggs as she sees fit for the needs of the entire colony.
Ant Larvae: After an egg hatches, the next stage of the ant life cycle is the larval stage. At this point, ants are still just blind, legless grubs that are completely dependent on worker ants to take care of and feed them. This stage generally lasts between one to two weeks. Transitions during this period, called molts, will occur as the ant develops. During the larval phase is when the second stage of ant caste selection occurs. Fertilized eggs will hatch into larvae that can develop into worker ants, soldier ants, or alates depending on the nutrition levels they are provided and the pheromones they are exposed to. Ant colonies generally have a split of 95% workers to 5% soldiers, which is controlled by a developmental inhibiting pheromone that soldier ants release. This causes an ant colony population to remain mostly workers if too many soldiers exist within a colony.
Ant Pupae: After molting is completed, the ant larvae will move to the pupae stage of the ant lifecycle. This is when the immature ants will look much more like their adult form. Even though they will have the primary structures mature ants have, they will still be largely immobile and will rest until mature. They will be much lighter in color and this last stage takes between one to four weeks. When this stage is completed, the ant will emerge as its final adult form in whichever caste is needed by the colony.
Adult Ant: A fully mature ant drone, worker, soldier, or alate will emerge from the pupal stage. It will have a hardened, darker exoskeleton and will be ready to play its role within the colony. At this point, the development of an ant has taken between one to two months. Anything beyond this period, an ant’s lifespan will largely depend on variables like the ant’s luck and resource availability.
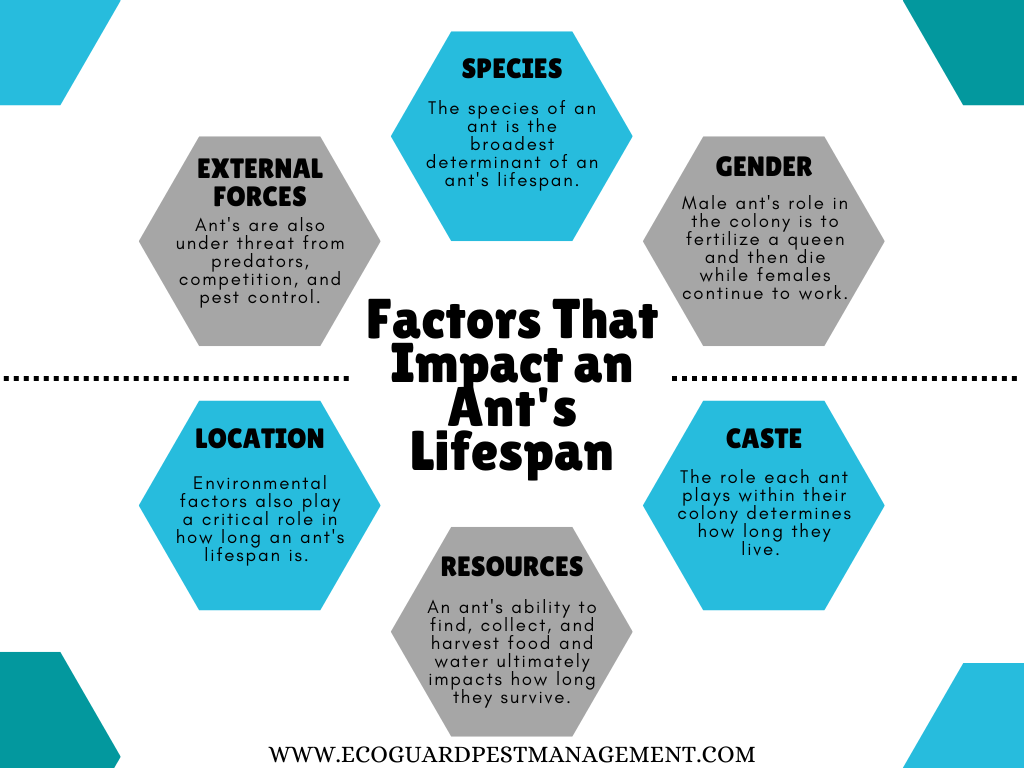
Factors That Impact an Ant’s Lifespan
The primary factors that determine an ants’ lifespan include:
- Ant species: Some ant species live extremely long lives while other ants’ lifespans can be as short as a few months.
- Ant gender: Male ants come from unfertilized eggs and become drones. A drone’s sole purpose is to fertilize a queen and then die. Due to this, a male ant’s life span is generally around a week after reaching maturity. Female ants on the other hand, make up a majority of the colony and can live up to a couple years depending on caste and species.
- Ant caste: Ant castes are determined by equal parts nature vs nurture. A queen will have a large role determining the sex of the eggs she lays by selectively fertilizing eggs. Afterwards, the caste of female ant larvae will be determined by the nutrition they are provided and the unique needs of the colony. Each role has a different lifespan which caters to the needs of colony.
- Available resources: A colony’s ability to sustain the ant population is critical to overall colony survival. In times of famine and drought, the colony suffers, and ants’ lifespans can be cut short from starving, thirst, or even cannibalism as the queen will feed on others to keep the colony alive.
- Location: While ants are durable and persistent, they are still subject to nature’s wrath. Location and ability to find adequate shelter from the elements will have an impact on how long an ant can survive. Locations that get too cold or too wet may decrease the lifespan of an ant by being too uninhabitable.
- Outside forces: There is always a chance that an ant’s life span is cut short by a predator, an attacking ant invader, conflict between ants and termites, or at the hands of a professional exterminator.
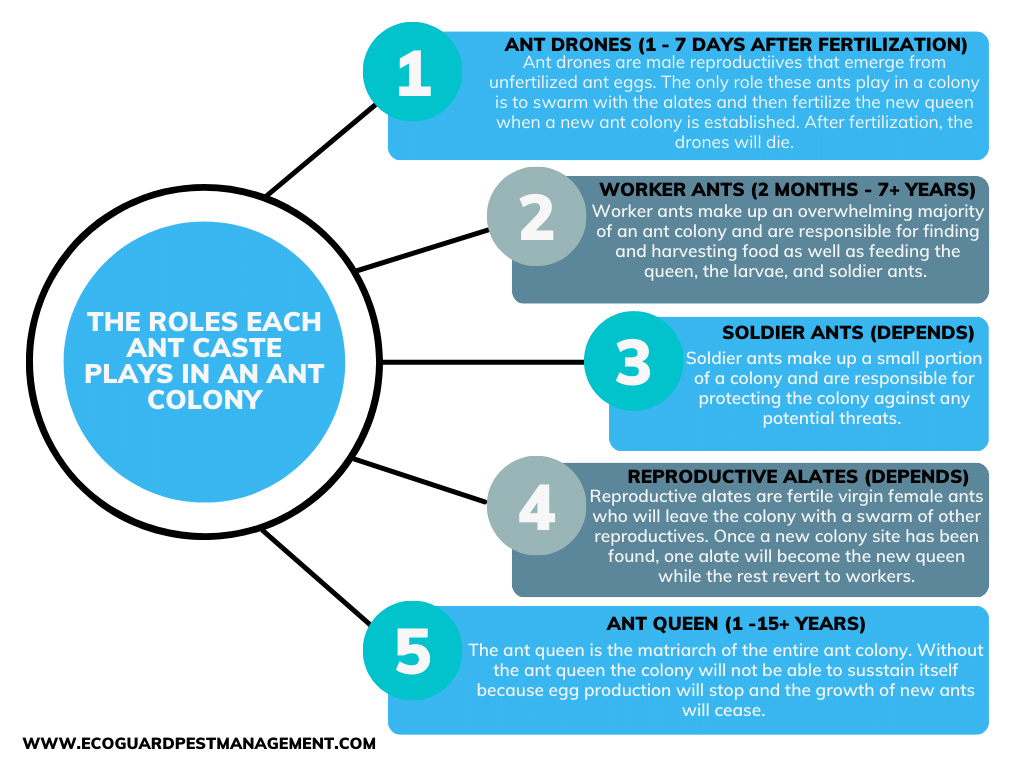
Caste Determines Ant's Lifespan
Ant caste plays a significant role in how long an ant will survive:
- Drones: Drones are males who only role in the colony is to fertilize eggs. They will die shortly after fertilization is completed.
- Workers: Worker ants make up 95% of a colony. Some colonies’ worker ants will live up to a couple years while others will only survive for a couple of months.
- Soldiers: Soldier ants, by nature of their role are usually killed off early in defense of the colony.
- Alates: Alates will live their lifespan developing into reproductives before swarming and moving to create a new colony. At that point, one of the females will become a new queen, while the rest of the females revert to workers and the males serve their purpose.
- Queen Ant: Ant queens live the longest of all ant castes. Her role is pivotal so she can’t be replaced
Species Affects Ant’s Lifespan
One of the biggest factors that affects an ant’s lifespan is the ant’s species. The variation between some ants’ lifespans is quite large with some species like carpenter ant workers surviving up to 7 years, while pharaoh ant workers typically survive for around 70 days.
| Ant Species | Worker Ant | Ant Queen |
|---|---|---|
| Argentine Ants | 10 - 12 Months | 10+ Years |
| Black Garden Ants | 4 Years | 15+ Years |
| Carpenter Ants | 7+ Years | 10+ Years |
| Fire Ants | 1 - 6 Months | 2 - 6 Years |
| Odorous House Ants | 2 - 6 mOnths | 1+ Year |
| Pavement Ants | 5 Years | 5+ Years |
| Pharaoh Ants | 70 Days | 4 - 12 Months |
| Thief Ants | 2 - 5 Months | 1+ Year |
Caste and Gender Determines Ant's Lifespan
Ant caste and gender plays a significant role in how long an ant will survive:
- Drones: Drones are males who only role in the colony is to fertilize the eggs of alates, or new reproductive queens. Drones make up one of the smaller groups within the ant colony and are only produced when a colony is ready to expand. When a colony reaches capacity, an ant queen will create unfertilized alates and drones that will take flight in search of a new place to colonize. After a new colony site is found, the drones will fertilize the new queen then die within 1 – 2 days after fertilization is completed. Other drones that are not selected to fertilize the queen will normally die off within 7 days of maturity.
- Workers: Worker ants make up 95% of a colony. Some ant colonies’ workers will live up to a couple years while others will only survive for a couple of months.
- Soldiers: Soldier ants make up roughly 5% of an ant colony These ants are bigger than worker ants and have large heads and mandibles designed to protect the ant colony. Due to the nature of their role, they are usually killed off early while defending the colony so measuring their average expected lifespan is difficult.
- Alates: Alates are essentially virgin female queens that emerge when a colony is ready to expand. These reproductive females will begin to swarm with the male drones before moving out in search of a place to create a brand-new colony. Once a location is discovered, one of the females will become a new queen, while the rest of the females revert to workers and drones die off.
- Queen Ant: Ant queens live the longest of all ant castes. Her role is pivotal in determining the outcome of an ant colony so she can’t be replaced.
How Long Does the Queen Ant Live?
Queen ants are the longest living ants in a colony. Because ant queens are so important to a colony, they are protected deep inside a colony near the chambers designed to house eggs and larvae. The queen ant is a colony’s only source of eggs and also controls the development of a colony so if the queen ant dies, a colony will typically die off shortly after. Depending on the species, some queen ants will live between 10 – 20 years with the longest living known ant queen surviving for 28 years.
Resources Impact Ant’s Lifespan
Resource availability also plays a role in how long ants survive. Normally worker ants are responsible for gathering the supply of food ants eat.
How Long Do Ants Live Without Food?
Much like any other living organism, ants can only go so far without food to sustain themselves. It is hard to measure the how long ants can survive without adequate food resources, but it is estimated that ant workers can forgo food 1 - 2 weeks before they succumb to starvation. In the event that there are not enough food resources to sustain a colony, the workers will endure food scarcity while still providing for the ant queen. The ant queen is the only member of the colony that is not expendable. If the ant queen dies, so does the colony. Before this happens, the ant queen will resort to cannibalizing eggs and larvae to sustain herself before starving.
How Long Do Ants Live Without Water?
Measuring how long ants can survive without water has proven difficult in the wild due to the abundance of water in almost every environment that ants are found in. Some experiments that have deprived ants of water have shown that ants can survive for approximately 5 days without water or hydration.
Contact EcoGuard Ant Exterminators Today
If you have seen signs of ant activity in or around your home, it may be time to enlist professionals from EcoGuard Pest Management to come inspect your property. Our licensed and experienced ant control experts will ensure that all the problematic areas are identified so you can get rid of your ant problem. We can create a customized treatment strategy guaranteed to exterminate your ant problem and implement preventative measures that will deter ants in the future.

















